手写实现迷你版Tomcat
MiniTomcat要做到的事:通过浏览器客户端发送的http请求,MiniTomcat在接收到请求并对其进行处理,处理之后,按照http协议返回给浏览器客户端。
- 提供服务,能够接收到浏览器的请求(Socket通信)
- 解析请求信息即请求的请求头等相关信息
- 将请求(响应)信息封装为一个Request对象(response对象)
- 客户端请求资源,资源分为静态资源(html等)和动态资源(servlet)
- 资源返回给客户端浏览器
手写实现迷你版Tomcat V1.0
浏览器通过请求地址,获取到浏览器请求的信息及返回一段字符串给客户端浏览器显示
BootStrap启动类:
public class BootStrap {
private int port = 8080;
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
/**
* MiniTomCat 启动需要初始化展开的一些操作
*/
public void start() throws IOException {
// Socket监听端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println(" ============> MiniTomCat start on port:" + port + "<==================");
// 循环监听客户端的请求
while (true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
// 从输入流中获取到请求信息,并解析,通过字符串输出
int count = 0;
while (count == 0){
count = inputStream.available();
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println("==========》 请求信息:" + new String(bytes));
// 相应数据
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
// 按照http协议设置响应头,此处两个详细信息必须存在,否则,客户端无法解析响应
outputStream.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK \n".getBytes());
outputStream.write("Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8 \n\r\n".getBytes());
outputStream.write("hello MiniTomCat!".getBytes());
socket.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BootStrap bootStrap = new BootStrap();
bootStrap.start();
}
}
获取到请求体信息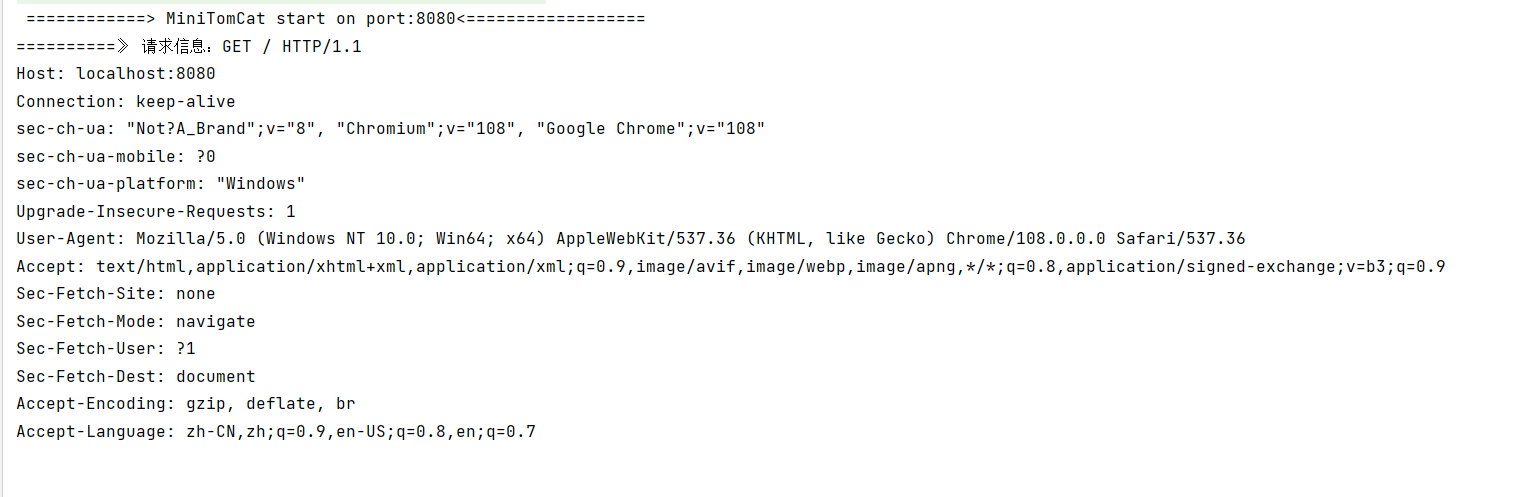
手写实现迷你版Tomcat V2.0
封装http协议返回数据格式的类,目前提供响应200及404
public class HttpProtocolUtil {
public static String getHttpHeader200(long contentLength) {
return "HTTP/1.1 200 OK \n" +
"Content-Type: text/html \n" +
"Content-Length: " + contentLength + " \n" +
"\r\n";
}
/**
* 为响应码404提供请求头信息(此处也包含了数据内容)
* @return
*/
public static String getHttpHeader404() {
String str404 = "<h1>404 not found</h1>";
return "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT Found \n" +
"Content-Type: text/html \n" +
"Content-Length: " + str404.getBytes().length + " \n" +
"\r\n" + str404;
}
}
封装Request及Response类
- request对象
public class Request {
private String method; // 请求方式 例如 get / post
private String url; // 请求的url
private InputStream inputStream; // 输⼊流,其他属性从输⼊流中解析出来
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return inputStream;
}
public void setInputStream(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
public Request() {
}
// 构造器,输⼊流传⼊
public Request(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
// 从输入流中获取到请求体信息
int count = 0;
while (count == 0){
count = inputStream.available();
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
inputStream.read(bytes);
String inputStr = new String(bytes);
// 获取第⼀⾏请求头信息
String firstLineStr = inputStr.split("\\n")[0]; // GET / HTTP/1.1
String[] strings = firstLineStr.split(" ");
this.method = strings[0];
this.url = strings[1];
System.out.println("=====>>method:" + method);
System.out.println("=====>>url:" + url);
}
}
- response对象
public class Response {
private OutputStream outputStream;
public Response() {
}
public Response(OutputStream outputStream) {
this.outputStream = outputStream;
}
// 使⽤输出流输出指定字符串
public void output(String content) throws IOException {
outputStream.write(content.getBytes());
}
/**
* @param path url,随后要根据url来获取到静态资源的绝对路径,进⼀步根据绝对路径
* 读取该静态资源⽂件,最终通过
* 输出流输出
* /-----> classes
*/
public void outputHtml(String path) throws IOException {
// 获取静态资源⽂件的绝对路径
String absoluteResourcePath =
StaticResourceUtil.getAbsolutePath(path);
// 输⼊静态资源⽂件
File file = new File(absoluteResourcePath);
if (file.exists() && file.isFile()) {
// 读取静态资源⽂件,输出静态资源
// 静态资源请求处理⼯具类
StaticResourceUtil.outputStaticResource(new
FileInputStream(file), outputStream);
} else {
// 输出404
output(HttpProtocolUtil.getHttpHeader404());
}
}
}
- 获取绝对路径的类
public class StaticResourceUtil {
/**
* 获取静态资源⽂件的绝对路径
*
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static String getAbsolutePath(String path) {
String absolutePath =
StaticResourceUtil.class.getResource("/").getPath();
String decode = URLDecoder.decode(absolutePath);
return decode.replaceAll("\\\\", "/") + path;
}
/**
* 读取静态资源⽂件输⼊流,通过输出流输出
*/
public static void outputStaticResource(InputStream inputStream,
OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
int count = 0;
while (count == 0) {
count = inputStream.available();
}
int resourceSize = count;
// 输出http请求头,然后再输出具体内容
// 动态资源请求
// Servlet接⼝定义HttpServlet抽象类定义
outputStream.write(HttpProtocolUtil.getHttpHeader200(resourceSize).getBytes());
// 读取内容输出
long written = 0;// 已经读取的内容⻓度
int byteSize = 1024; // 计划每次缓冲的⻓度
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteSize];
while (written < resourceSize) {
if (written + byteSize > resourceSize) { // 说明剩余未读取⼤⼩不
//⾜⼀个1024⻓度,那就按真实⻓度处理
byteSize = (int) (resourceSize - written); // 剩余的⽂件内容⻓度
bytes = new byte[byteSize];
}
inputStream.read(bytes);
outputStream.write(bytes);
outputStream.flush();
written += byteSize;
}
}
}
手写实现迷你版Tomcat V3.0
3.0版本,实现通过解析web.xml文件,来将servlet标签动态添加到一个map中,客户端发送请求时,通过请求的url拿到对于的servlet处理类,来处理对应的请求



评论区